Flexible PCBs
Flexible printed circuit boards are ideal for tackling complex geometric tasks and offer a high degree of design freedom for everyday engineering work. Low space requirements, low weight and reduction of system costs by saving cables and connectors in device assembly are just some of the advantages of flexible PCBs.
Possibilities with flexible PCBs
Flexible printed circuit boards, also known as FPCs (Flexible Printed Circuits), allow electronic components to be placed in three-dimensional configurations, which is important in applications where space and form factor are critical.
The flexible substrate material, usually polyimide (Kapton), allows the circuit board to be bent and folded with the smallest possible bending radius. The required sizes range from very small and narrow flexes of <1 mm in size to large and long applications, which are then manufactured as long flexes several meters in length.
The design options are also more varied than with other technologies: In addition to single-layer and double-layer FPCs with and without stiffeners, there are flexible multilayers usually with shielding layers, with impedances, with contacting from one side, made of high-temperature material and much more.
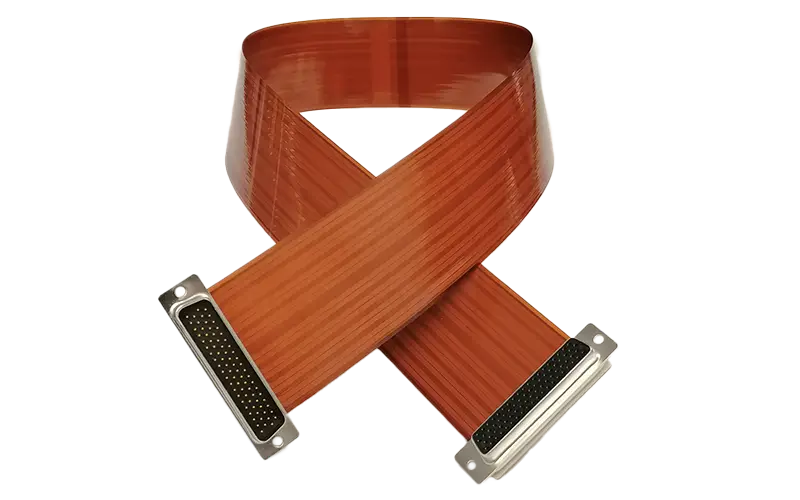

Our materials, technologies and tolerances
Maximum Dimensions
470 × 575
mm
9–140
µm
Base films
12–150
µm
Structure
Glueless + with acrylic
Up to
14
layers
In use in
DLR / NASA / ESA
projects
Add Ons
- Stiffener
- ZIF plug
- Hard gold contacts
- Adhesive foils
- Fanned out
- Two-sided access
- Stable THT solder fingers
- Heating structures
- Heatsinks
For a complete list of our flex PCB fabrication capabilities, please refer to our capabilities section:
Some references
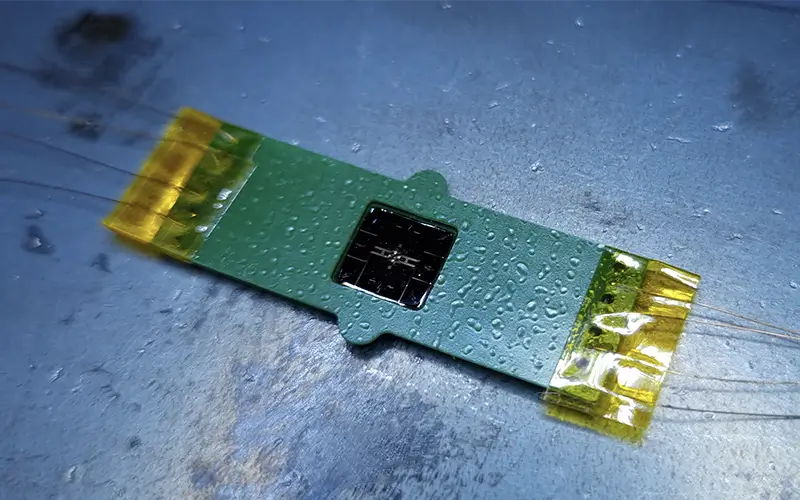

Semiflex printed circuit board with superconducting conductor tracks
For the investigation of quantum effects using quantum optical methods. The aim is to achieve control over the states of motion of quantum systems. The conductors lose their electrical resistance above a certain minus temperature.
Production guidelines for multilayer printed circuit boards
We manufacture printed circuit boards according to IPC-6013 / IPC-A-600 in the following IPC classes:
Class II is for general industrial production, i.e. appliances that are subject to higher demands and require high performance and a long service life.
Electronics in which continuous, uninterrupted operation is of crucial importance, for example in life-sustaining medical technology, in aircraft electronics such as flight controls and in safety-relevant applications.
Documentation and traceability of the entire production chain
We carry out the following tests:
- Electrical test according to IPC-9252
- Impedance control (TDR measurement method)
- Resistance measurement
- Milliohm measurement: four-wire method
- High-voltage test up to 500V
- EMPB (initial sample test report) with dimensions
- Layer thickness measurement (X-Ray)
- Micrograph analysis after solder shock test
- Solderability
- Preparation of CoC (Certificate of Conformity)
- Customer-specific tests by arrangement
- Application-specific tests by arrangement
Let us advise you free of charge!
We will be happy to help you:

Dr. Christoph Lehnberger
Head of Technology

Patrick Peek
Head of Sales
Frequently asked questions about flexible printed circuit boards
What are flexible printed circuit boards?
Flexible printed circuit boards, also known as FPCs (Flexible Printed Circuit), consist of one or more thin, flexible foils laminated with copper as a carrier for the production of electronic circuits. In contrast to FFCs, where straight conductors are laminated in parallel between two foils, FPCs can be individually structured and assembled like rigid PCBs. With flexible printed circuit boards, components can be placed in three-dimensional configurations, which is advantageous when space and form factor are limited. The flexible polyimide material can be bent and folded, depending on the bending radius for installation or dynamically for permanent movement.
What are the properties and advantages of flexible printed circuit boards?
- Flexibility: They can be bent or folded into different shapes.
- Space-saving: Their flexible nature makes them ideal for compact electronics.
- Light and thin: They offer a lower mass compared to rigid PCBs.
- Vibration resistant: They withstand mechanical stress and are more resistant to vibrations.
- Reduced connection points: Fewer solder joints reduce potential failure points and improve reliability.
What are flexible printed circuit boards used for?
- Medical devices: Implantable and wearable devices require flexible solutions.
- Automobile industry: For sensors, control units or displays that often work in confined spaces.
- Electronic devices: Mobile phones, tablets and wearables benefit from space savings.
- Aerospace: Flexibility and lightweight construction are particularly important in these areas.
- Industrial electronics: Machine controls and robots, where mobility and adaptability are required.
How are flexible printed circuit boards manufactured?
- Substrate material: Use of flexible materials such as polyimide or polyester.
- Etching the conductor tracks: Copper is applied to the substrate and etched into the desired layout.
- Lamination: Protective layers are added to insulate the copper conductors.
- Drilling holes and mounting components: Vias and components are applied.
- Testing: Each PCB is tested for functionality and defects.
What do you have to look out for during production?
- Design layout: Flex PCBs require special design rules to take bending radii and mechanical loads into account.
- Material selection: Materials must be used that are not only flexible, but also heat resistant and electrically insulating.
- Soldering processes: It must be ensured that the flexible material is not damaged at high temperatures.
- Durability: Repeated bending can lead to mechanical stress in the long term, which must be taken into account.

